US climate bill & grid modernization: What you need to know about the new US bill and what it means for power grid monitoring.
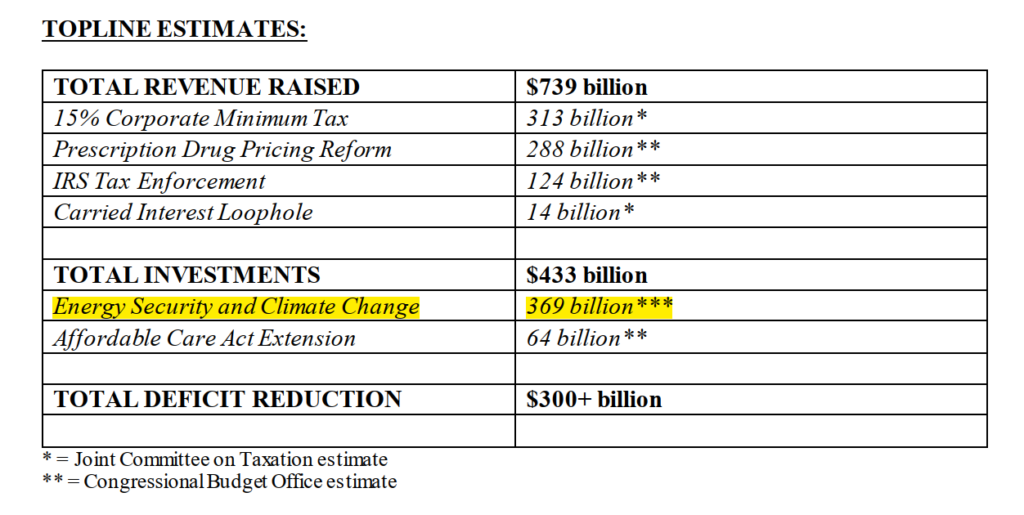
The US Senate and congress recently passed a significant bill, the Inflation Reduction Act of 2022, in August 2022. However, the bill’s name hides what can be viewed as the biggest move that the United States of America has ever made to address climate change. While the bill does deal with healthcare and taxing corporations, the biggest share of the bill’s spending is climate and clean energy – $369 Billion over 10 years.
Here are some estimates for the allocated budgets:
Source: The inflation reduction act of 2022 summary
The bill passed the house (on August 12th, 2022) and moved to President Biden’s desk to be signed into law soon. It represents a major move for grid modernization, providing unprecedented funding to ensure energy security, reduce carbon emissions, increase energy innovation, and support environmental goals.
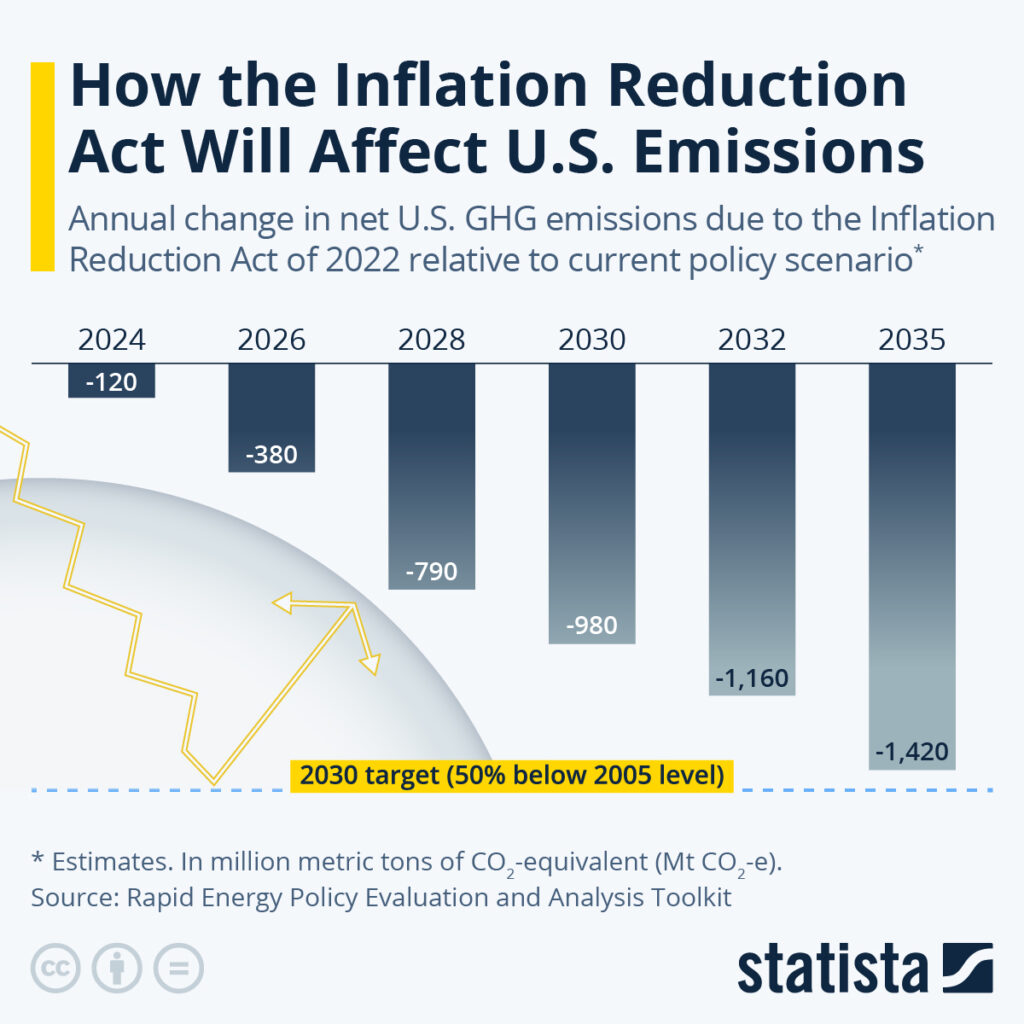
But if truth be told, it seems that the administration’s emissions goal of reaching 50 percent of the 2005 level by 2030 seems rather ambitious. Nonetheless, it is undoubtedly a move in the right direction.
Even though the US annual greenhouse gas emissions are expected to be significantly lower by 2030 than they would be if the country’s current policies were maintained, the data from Rapid Energy Policy Evaluation and Analysis Toolkit (REPEAT) estimates indicate that the target is still far off. Instead, REPEAT expects emissions to come closer to the desired level by 2035.
Source: Statista
What about the transmission grid?
The Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) refers to the power transmission grid in several ways. The prominent ones include:
- Grid modernization through the deployment of new interstate transmission lines
- Creating clean energy generation and the needed transmission
- Supporting the innovation and deployment of new transmission technologies with tax laws
Enhanced transmission grid
The IRA views an enhanced U.S. transmission system as key to enabling increased use of wind and solar energy for electricity generation and improving resilience to extreme weather events. Recent years have shown that strong winter storms can cripple the power transmission system and cause serious damage. Just look back at the 2021 winter storm Uri which impacted the US, Canada, and northern Mexico.
For that, there are allotted grants to facilitate the siting of interstate electricity transmission lines in previously suggested transmission corridors (see section 50152 of the IRA for details). This aims to build a stronger and more resilient power grid. There are also loans to develop rural transmission lines for better coverage of rural areas.
Cleaner energy needs transmission as well
While there is a strong push in the energy sector toward cleaner energy generation via solar and wind power, many miss the fact that these require additional power transmission lines, as well as modernization of the current grid and better grid monitoring. More onshore and offshore power transmission is needed to move energy from the remote generation areas to consumers. The IRA bill addresses this by directing allocated grants for Interregional and offshore wind electricity transmission planning, modeling, and analysis (section 50153 of the bill).
Paving the way for new grid technologies
The bill contains a range of incentives and tax credits to drive emissions-free energy, among other things. For example, the IRA tax credits will be in place for 10 years to finance new technologies and make innovation and grid modernization easier.

Quoting the Senate Finance Committee Chair Ron Wyden responded to the bill’s approval – “For the first time, the tax code is going to reward emissions reductions, and encourage the development of new clean energy technologies as soon as they come online. No longer will Congress need to legislate technology by technology, making it easier to innovate and bring new technologies to market. Importantly, this is a permanent energy policy. Congress will no longer need to extend these incentives every few years, giving companies and states certainty to plan clean energy projects and create jobs.”
PrismaPower, taking grid monitoring and optimization to the next level
PrismaPower fits the bill. Allowing transmission operators to monitor their network for hundreds and even thousands of miles without installing anything on the power grid itself. Using the existing optical fibers, which are part of most modern networks, it is a solution that scales to the power grid size.
Used by the New York Power Authority, the Israel Electric Company, and others, transmission system operators (TSOs) can monitor and optimize their network, alerting for any physical damage to the powerlines, whether overhead or underground. In addition, Corona levels are tracked along the lines, stating where maintenance is needed and alerting to high levels before anything harmful can happen – thus helping in the effort to reduce emissions and optimize the power network. Extreme weather conditions, icing, strong winds, and wildfires are also monitored, with PrismaPower alerting to specific locations, making the grid more resilient and better equipped to handle severe conditions brought forward in recent years.
PrismaPower keeps collecting data on the grid, 24×7, in any weather, all the time. This is the key to digitalization and grid monitoring and overall grid modernization. It is part of the tools that the IRA bill talks about when it raises the hope for the change that will help future generations.
To Summarize
The Inflation Reduction Act of 2022 is a large move towards a better and cleaner energy future, made from thousands and more small steps. There is no one keystone that makes a fundamental difference, but it is clear that improving the existing infrastructure and using the new tools and technologies that keep springing up. The sum of all these can and will make a change. To quote Archimedes, that ancient Greek mathematician, “Give me but one firm spot on which to stand, and I will move the earth.”
Read more on PrismaPower and its unique grid monitoring abilities.